Is rolling required during simultaneous gravel seal construction?
Is rolling required during simultaneous gravel seal construction? This problem is a technical one. But in order to cater to the needs of the majority of users, the editor is here to chat about it for everyone!
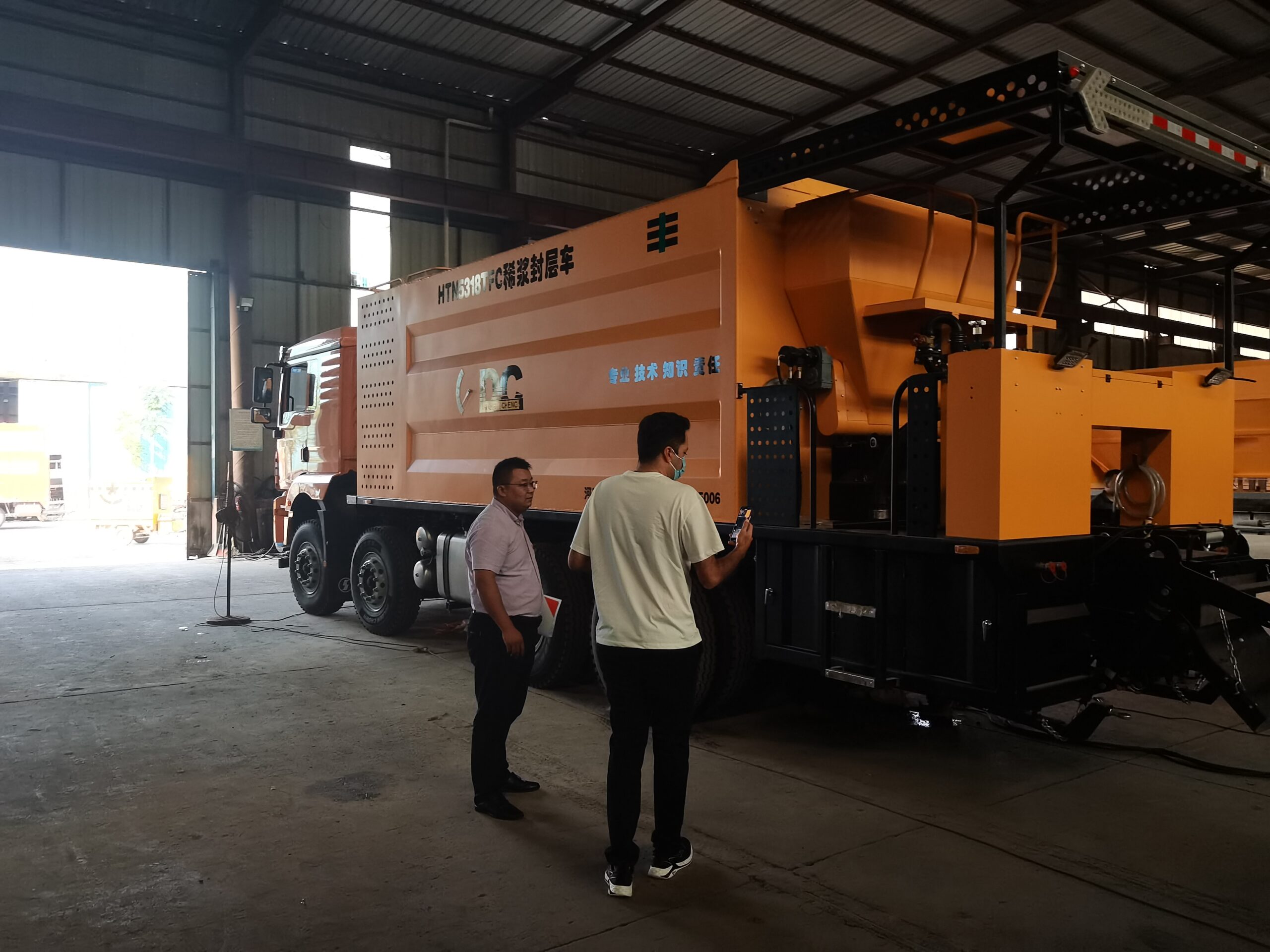
Synchronous gravel sealing uses special equipment – the synchronous gravel sealing truck to spread asphalt binder and aggregates of a single particle size onto the road surface at the same time. Under the rolling of the rubber tire roller, the binder and aggregate are The asphalt gravel layer formed by sufficient bonding between them.
From the above definition of synchronous gravel sealing layer, we can easily see that synchronous gravel sealing layer needs to be rolled. So how to crush it?
In fact, whether the synchronous gravel sealing layer is rolled or not depends on what type of synchronous gravel sealing layer it is. If it is a synchronous gravel seal with non-emulsion type binder, use it; if it is a synchronous gravel seal with emulsion type cement, you have to choose it yourself.
crush
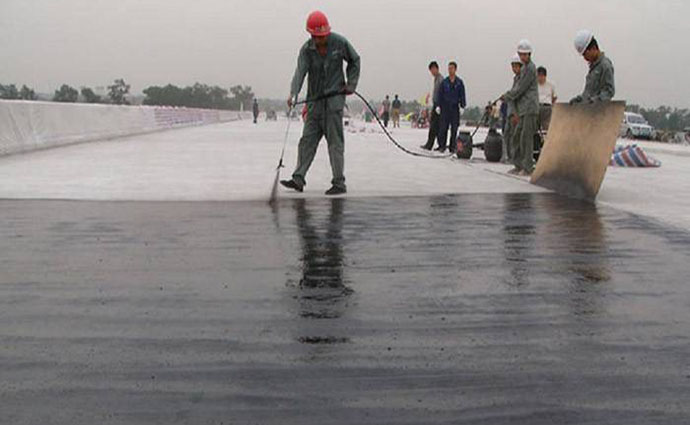
1. For simultaneous gravel sealing with non-emulsion binder materials, after spreading the gravel, use a rubber-tired road roller to quickly roll it over the entire width. The distance between the road roller and the spreading truck shall not exceed 15cm; then use a rubber wheel The road roller re-compacts 2 to 3 times, the rolling speed is controlled at 2.0km/h~2.5km/h, and the rolling wheel tracks overlap by about 30cm each.
2. For emulsion type binder materials, rolling is generally not required. If necessary, it can be rolled with a rubber tire roller before the emulsion is demulsified.
Note: (Rolling should use a rubber-tyred roller of more than 26t; the roller should avoid being on the same section each time it turns back. The roller should not brake or turn around at will during the rolling process. After 1 day of rolling, clean the surface with cleaning equipment or manually of pumice.)
crushing effect
After rolling, it is advisable that the asphalt and aggregate are fully bonded and there is no floating gravel on the surface.
Is the simultaneous gravel sealing layer required to be rolled during the construction process? If it is a non-emulsion type adhesive material, it is required; if it is an emulsion type adhesive material, it can be used or not.