Reasons for the reduction of heating efficiency of asphalt conveying pipes in asphalt mixing plants
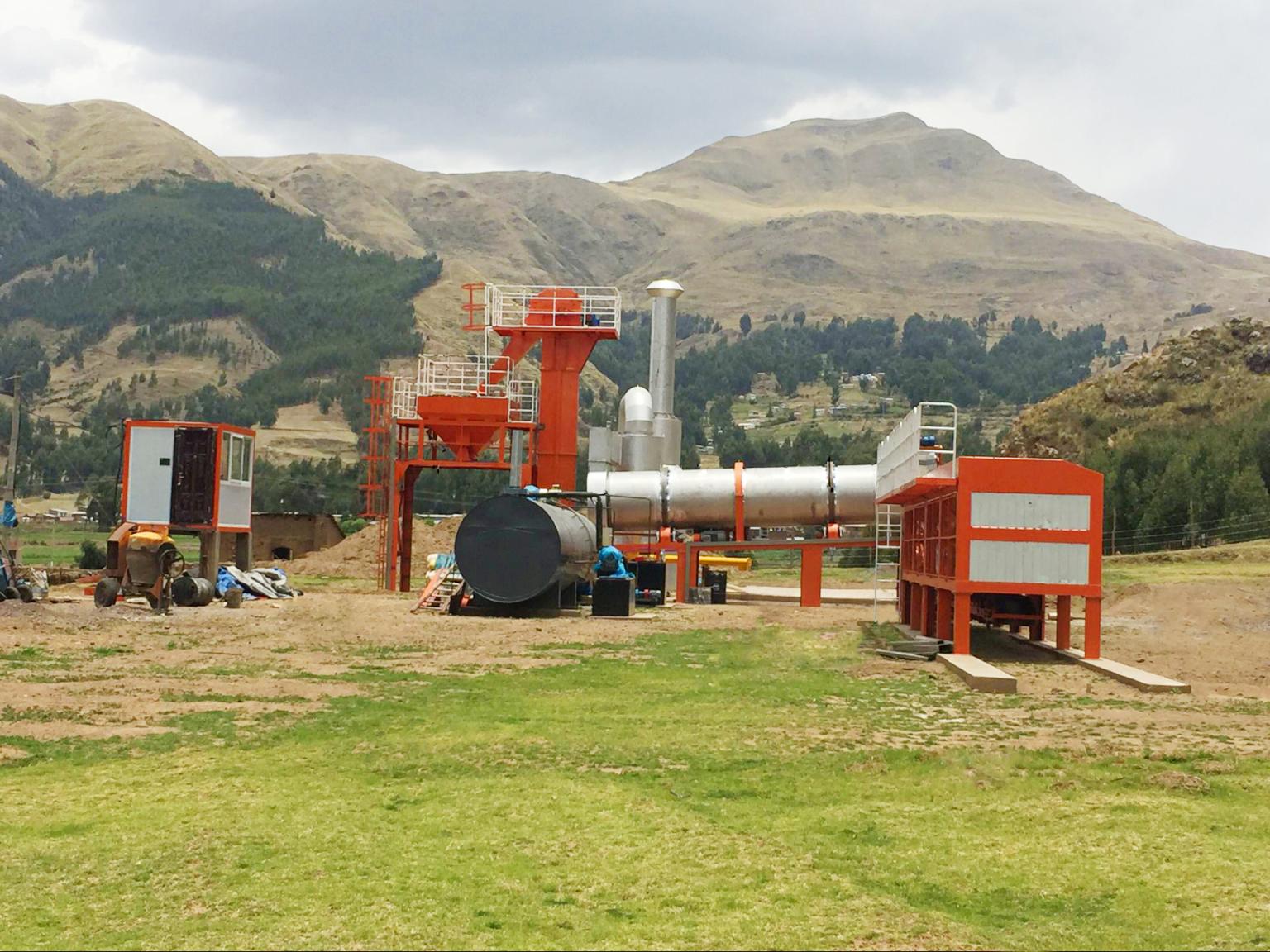
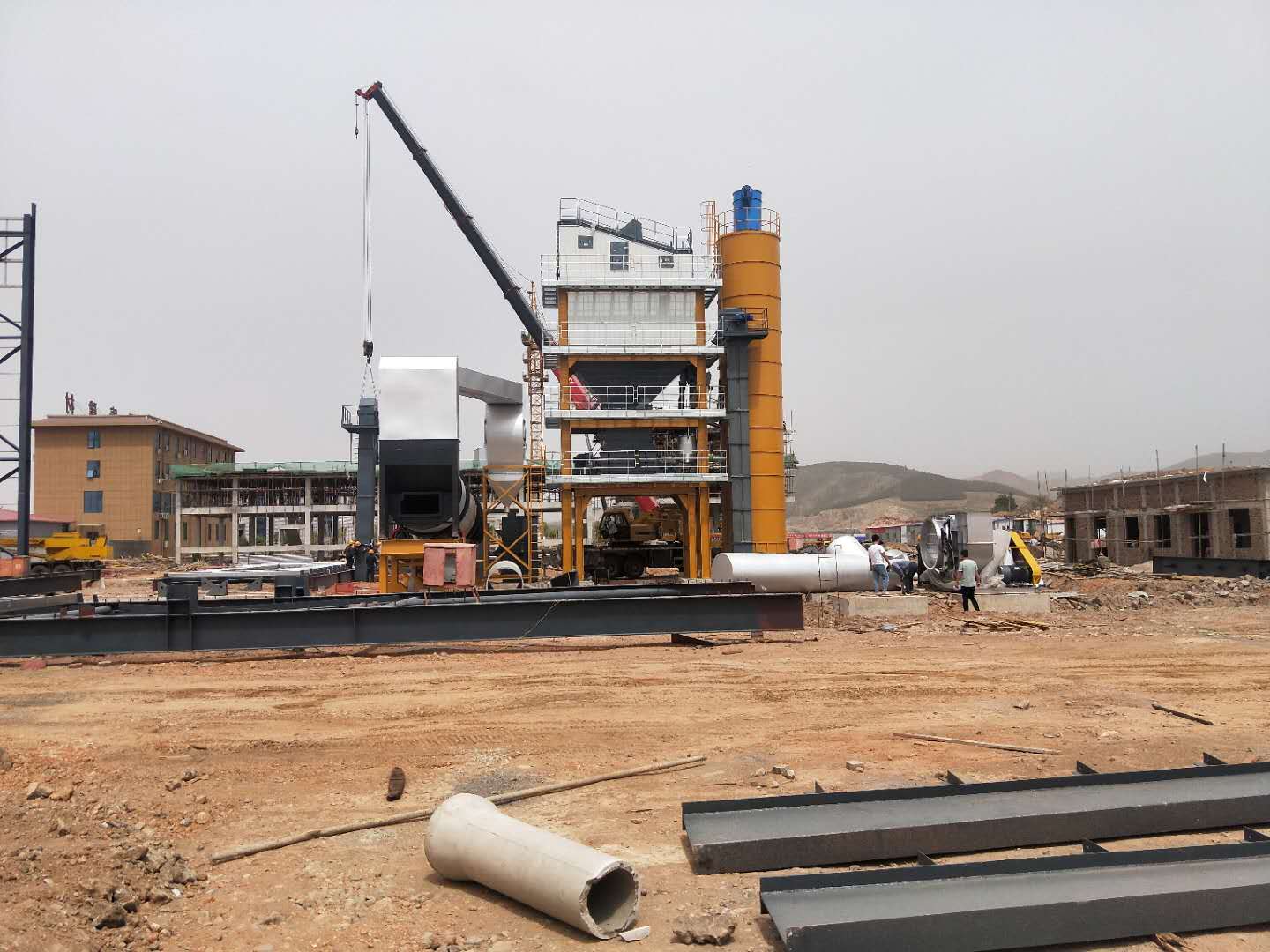
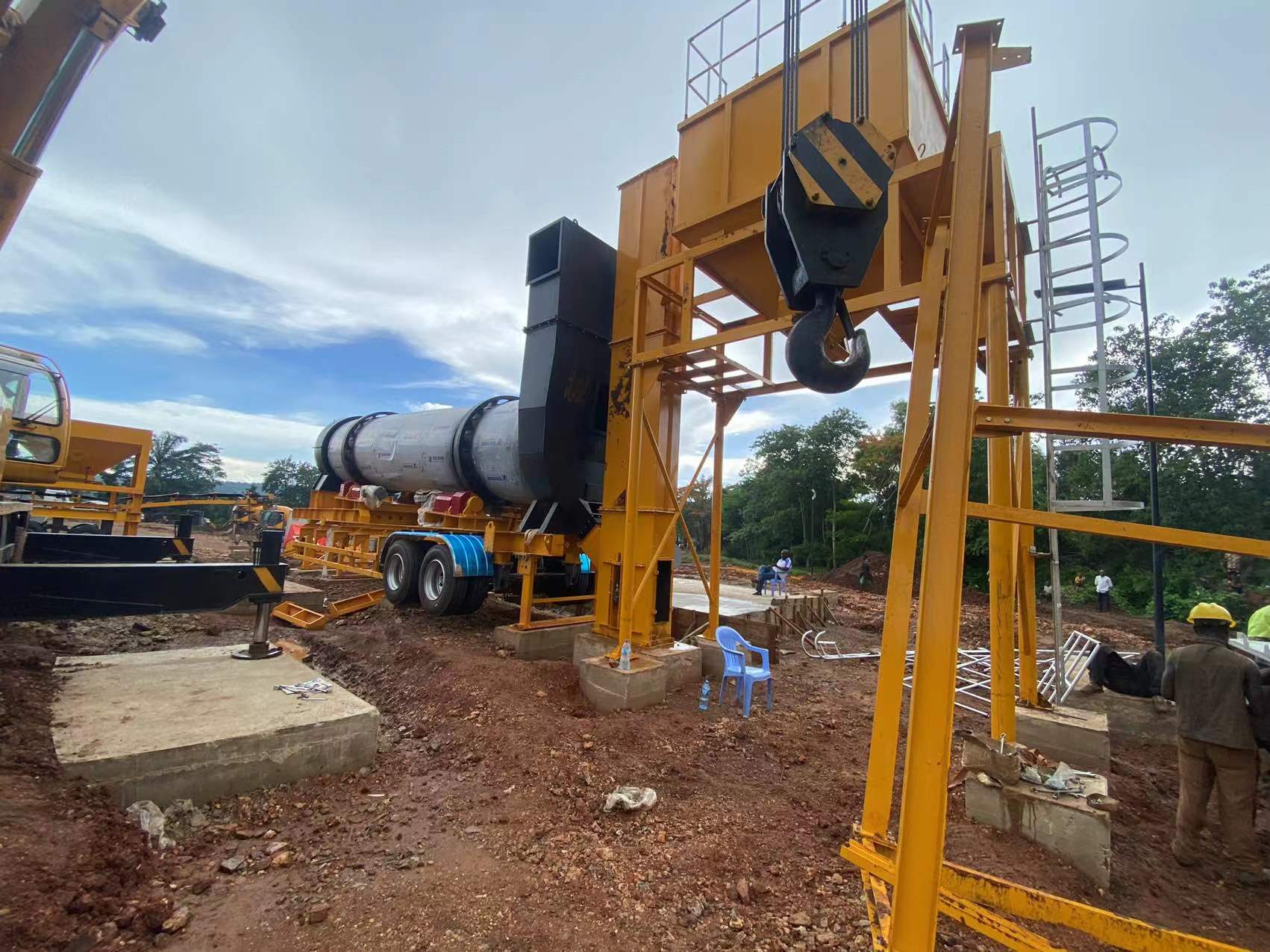
When inspecting the asphalt mixing plant, it was found that the asphalt in the pipeline solidified because the temperature of the asphalt transportation pipeline did not meet the requirements. Analysis believes that the reasons for this result are that the high-level oil tank of the heat transfer oil is too low, resulting in poor circulation of the heat transfer oil; the second is that the inner tube of the double-layer pipe is eccentric; the third is that the heat transfer oil pipeline is too long; and the fourth is that the heat transfer oil pipeline is not insulated measure.
When inspecting the asphalt mixing plant, it was found that the asphalt in the pipeline solidified because the temperature of the asphalt transportation pipeline did not meet the requirements. Analysis believes that the reasons for this result are that the high-level oil tank of the heat transfer oil is too low, resulting in poor circulation of the heat transfer oil; the second is that the inner tube of the double-layer pipe is eccentric; the third is that the heat transfer oil pipeline is too long; and the fourth is that the heat transfer oil pipeline is not insulated measure.
The high-level oil tank of the thermal oil is less than 3m away from the ground, while the high-level heat transfer oil circulation pipe is up to 5m away from the ground. When the asphalt mixing plant is finished working, due to the height difference, all the heat transfer oil in the high circulation pipe returns to the high heat transfer oil tank, and at the same time a large amount of air enters the heat transfer oil circulation pipe.
When the asphalt mixing plant resumes operation, the thermal oil circulation pump cannot completely drain the residual air in the high-altitude thermal oil circulation pipe, resulting in air blockage, which leads to poor circulation of the thermal oil and affects the heating effect. The asphalt conveying pipe of the asphalt mixing station adopts a double-layer pipe structure, that is, the outer pipe is heated by heat-conducting oil and the inner pipe transports asphalt.
After disassembling the asphalt delivery pipe, it was discovered that the inner pipe was not welded to the center of the outer pipe when the double-layer pipe was made, resulting in the inner pipe being eccentric. At the flange where the asphalt delivery pipe is connected, the joint of the heat transfer oil connecting pipe is welded exactly on the side of the eccentric tube with a smaller gap, which results in a reduction in the flow of heat transfer oil at the joint.
The residual welding slag and impurities from the production of asphalt conveying pipes are deposited in the small gaps at the eccentricity, causing a sharp reduction in the flow of thermal oil at the joints, resulting in a reduction in the heating efficiency of the thermal oil in the asphalt conveying pipes. If the heat transfer oil pipeline is too long, the delivery pressure at the end of the heat transfer oil pipeline will be insufficient, and the heat transfer oil at the end of the pipeline will cool down too quickly. When the ambient temperature is low, heat transfer oil pipelines without insulation measures will intensify the heat loss of the heat transfer oil.